The microwaves cause the water molecules in the food to vibrate. This generates heat and cooks the food.
How Do Microwave Ovens Work?
If you’ve ever heated up a frozen pizza or bowl of soup in the microwave, you’ve experienced firsthand how this commonplace kitchen appliance can cook food. But have you ever wondered exactly how microwaves cook food? It turns out that microwaves are pretty fascinating, and their ability to quickly cook food is thanks to some pretty amazing science.
Here’s a quick rundown on how microwaves work: Microwaves are a type of electromagnetic radiation, which means they are waves of energy that travel through the air (or any other medium). These waves are produced by an electric current, which is why your microwave has an electrical cord. When microwaves hit certain substances, like water molecules, they cause these molecules to vibrate.
This vibration creates heat, and it is this heat that cooks your food.
So there you have it! The next time you zap something in the microwave, remember that you’re harnessing the power of electromagnetism to cook your food.
Not bad for a little appliance that fits on your countertop.
How Do Microwaves Work
How Do Microwaves Work?
Microwaves are a type of electromagnetic radiation, which means they are waves of energy that travel through the air. They are similar to radio waves, but have a shorter wavelength and higher frequency.
This means they can carry more energy than radio waves, and can heat up food very quickly.
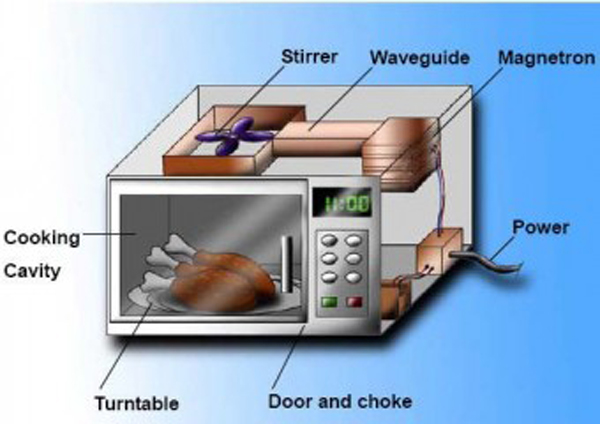
Microwaves are produced by an electric device called a magnetron. The magnetron takes electricity from the power outlet and turns it into microwaves.
The microwaves are then sent out into the oven chamber, where they bounce around until they hit the food.
The microwaves cause the water molecules in the food to vibrate back and forth at a very high speed. This makes the molecules rub against each other, creating heat.
The heat is then transferred to the rest of the food, cooking it evenly from all sides.

Credit: www.bbc.com
Does a Microwave Cook from the Inside Out?
There is a lot of debate surrounding this topic, with many people believing that microwaves cook food from the inside out. However, there is no scientific evidence to support this claim. Instead, it is more likely that microwaves cook food evenly throughout.
This is because microwaves heat water molecules directly, causing them to vibrate and create heat energy. So, while microwaves may not cook food from the inside out specifically, they do provide an even and efficient cooking method.
Can You Actually Cook in a Microwave?
Yes, you can actually cook in a microwave. A microwave oven is a type of electric oven that uses microwaves to heat food. Microwave ovens are very popular and are used by millions of people around the world.
Microwave ovens work by using microwaves to heat food. Microwaves are a type of electromagnetic radiation. When microwaves hit food, they cause the water molecules in the food to vibrate.
This vibration produces heat, which cooks the food.
Microwave ovens are very efficient at cooking food quickly and evenly. They can be used to cook all sorts of foods, including meats, vegetables, desserts, and more.
If you’re looking to cook something in a hurry, then a microwave oven is definitely the way to go.
How Do Microwaves Cook So Fast?
Most people are familiar with the microwave oven, which uses microwaves to cook food quickly. But how do microwaves actually work? And how do they cook food so fast?
Microwaves are a type of electromagnetic radiation, just like visible light and radio waves. They are produced by electric and magnetic fields that vibrate at a very high frequency. When these waves hit an object, they cause the molecules in that object to vibrate.
The vibration of the molecules causes them to produce heat, and it is this heat that cooks the food. Microwaves can penetrate food more deeply than other types of electromagnetic radiation, so they can cook food faster.
So there you have it!
Microwaves work by causing the molecules in food to vibrate, which produces heat and cooks the food quickly.
How Does Microwave Processing Work?
Microwave processing is a technology that uses microwaves to heat or cook food. Microwaves are a type of electromagnetic radiation, and when they are used to cook food, they cause the water molecules in the food to vibrate. This vibration produces heat, which cooks the food.
Microwave processing can be used to cook whole meals, or just certain ingredients in a meal. For example, microwave ovens can be used to cook meat, fish, vegetables, and pasta. In addition, microwave ovens can be used to reheat leftovers or frozen foods.
One advantage of microwave cooking is that it is very fast. For example, a frozen pizza can be cooked in about 3 minutes using a microwave oven. Other cooking methods such as baking or frying take much longer.
Another advantage of microwave cooking is that it is very convenient. You can set the timer on your microwave oven and walk away while your food cooks itself. This is especially helpful if you are short on time or if you want to avoid standing over a hot stovetop.
A disadvantage of microwave cooking is that it can sometimes result in uneven heating of food. This means that some parts of the food may be overcooked while other parts may be undercooked. To avoid this problem, it is important to stir or rotate the food during cooking so that all parts are exposed to the microwaves evenly.
In general, microwave processing is a quick and convenient way to cook food.
Conclusion
Microwaves cook food by using electromagnetic radiation to create heat. This process is called dielectric heating, and it happens when the microwaves cause the water molecules in food to vibrate. As the molecules vibrate, they create heat, which cooks the food.
Microwaves are a type of electromagnetic radiation, which means they travel through the air at the speed of light. Microwaves have a shorter wavelength than visible light, and they are absorbed by materials that are good at conducting electricity, like metal. When microwaves hit these materials, they cause them to vibrate, and this produces heat.